What is silicon carbide?
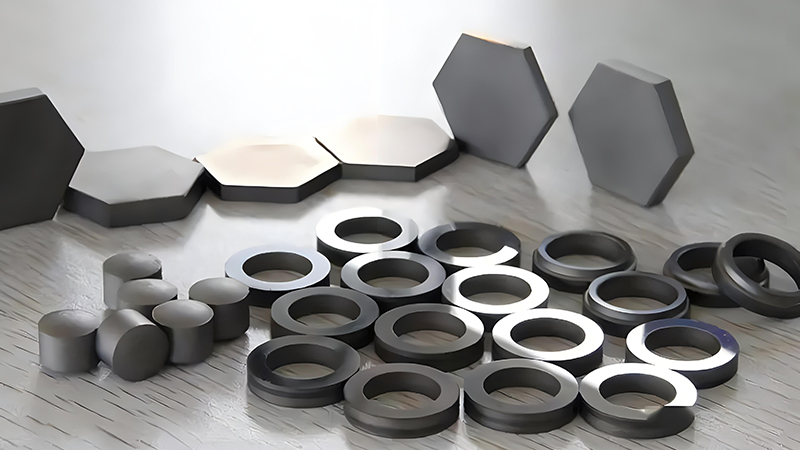
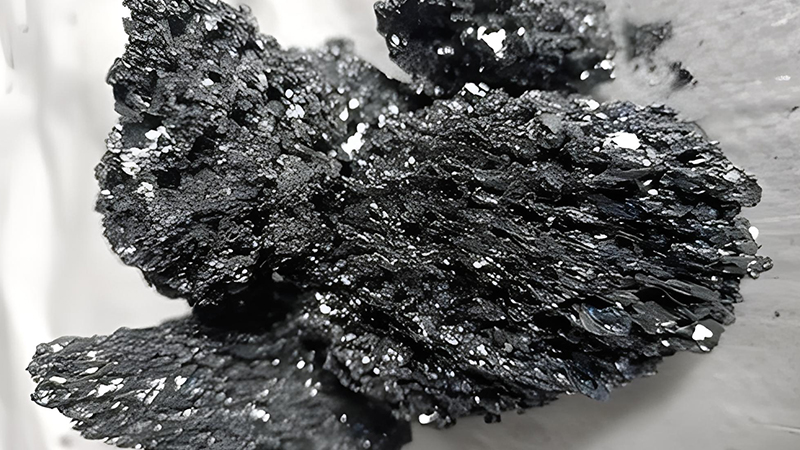
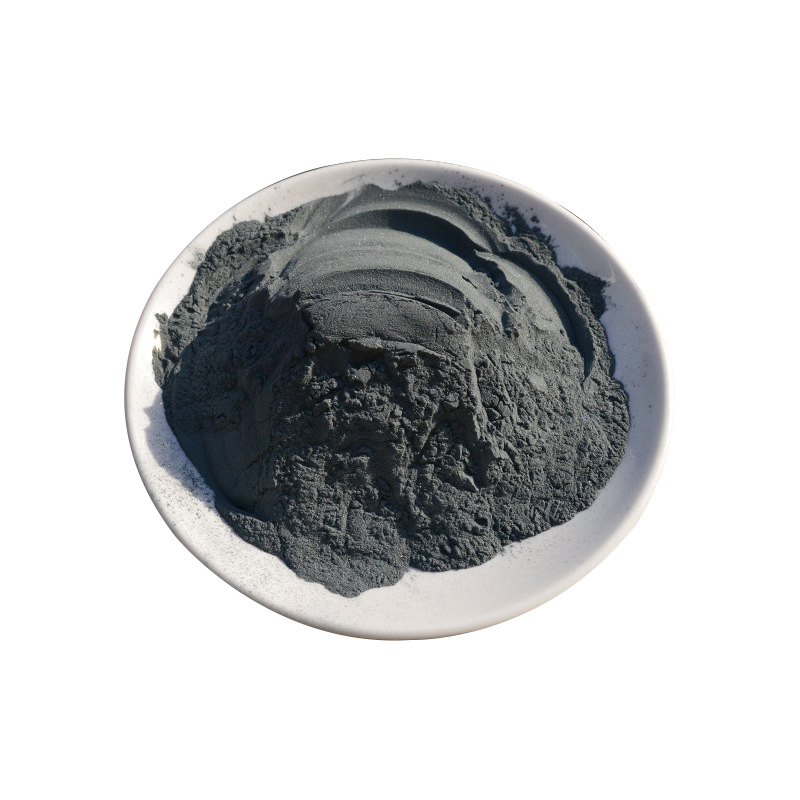
Silicon carbide is an inorganic substance with the chemical formula SiC. It is produced by high-temperature smelting of raw materials such as quartz sand, petroleum coke (or coal coke), wood chips (which require adding salt to produce green silicon carbide) through a resistance furnace. Silicon carbide is a semiconductor that exists in nature in the form of an extremely rare mineral, musonite. Since 1893, it has been mass-produced into powders and crystals, used as abrasives, etc. Among non oxide high-tech refractory raw materials such as C, N, and B, silicon carbide is the most widely used and economical one, which can be called gold steel sand or refractory sand. The silicon carbide produced by Chinese industry is divided into two types: black silicon carbide and green silicon carbide, both of which are hexagonal crystals.
Mosonite in nature only exists in very small amounts in certain types of meteorites, corundum deposits, etc. Currently, most of the silicon carbide sold worldwide, including mosonite jewelry, is synthetic.
In 1893, Maussanite first discovered naturally occurring forms of silicon carbide in meteorites from Arizona, and in 1905, this material was named Maussanite. [5] But Dr. Mosan's discovery was initially questioned because his sample may have been contaminated by silicon carbide saw blades that were already on the market at the time. [6]
Silicon carbide is rare on Earth, but common in space. The discovery of silicon carbide in space and meteorites is mostly β- SiC. The analysis of SiC particles found in the Murchison meteorite shows an abnormal ratio of carbon and silicon isotopes, indicating that these particles originated outside the solar system.
Previous: No More